Decoding the ICD-10 Code for Oral Thrush: A Comprehensive Guide
Are you searching for clarity on the ICD-10 code for oral thrush? Navigating the world of medical billing and coding can be daunting, especially when dealing with specific conditions like oral thrush. This comprehensive guide provides an in-depth look at the ICD-10 code for oral thrush, offering valuable insights for healthcare professionals, medical coders, and anyone seeking a better understanding of this condition. We aim to provide an authoritative and trustworthy resource that goes beyond simple definitions, exploring the nuances and practical applications of this important code.
Understanding the Basics of ICD-10 Coding
The International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision (ICD-10) is a globally recognized diagnostic coding system used to classify and code all diagnoses, symptoms, and procedures recorded in conjunction with hospital care in the United States. It’s essential for accurate medical billing, research, and tracking of health trends. The ICD-10 system provides a standardized language that ensures consistent communication across healthcare settings. Understanding the basics of ICD-10 is crucial for anyone involved in healthcare administration or clinical practice.
It is important to distinguish between ICD-10-CM (Clinical Modification), which is used for diagnosis coding, and ICD-10-PCS (Procedure Coding System), which is used for inpatient hospital procedure coding. When we discuss the ICD-10 code for oral thrush, we are referring to the ICD-10-CM code.
The Specific ICD-10 Code for Oral Thrush: B37.0
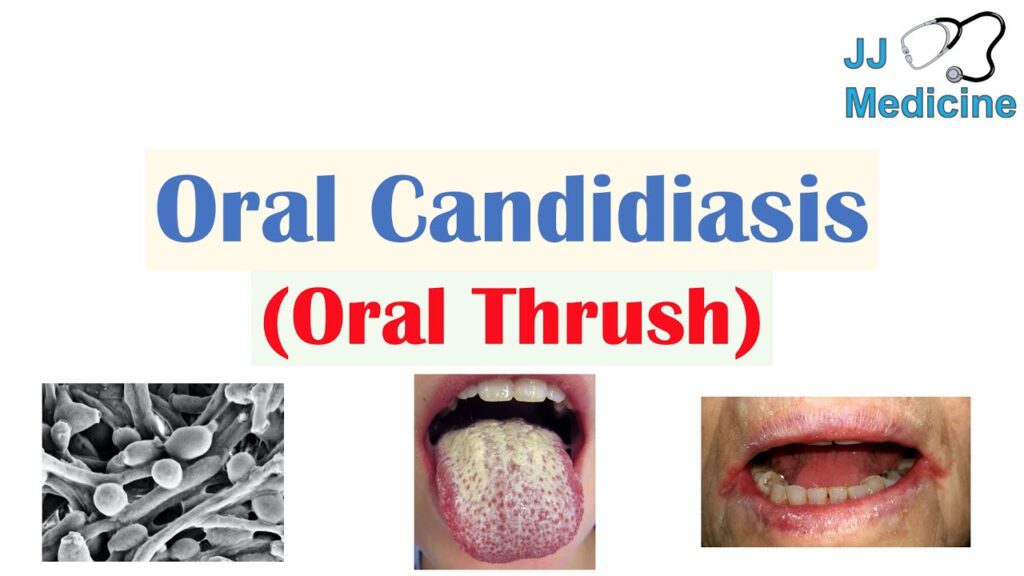
The ICD-10 code for oral thrush is B37.0. This code falls under the category of ‘Candidiasis,’ which encompasses infections caused by the Candida fungus. Specifically, B37.0 denotes ‘Candidal stomatitis,’ which is the medical term for oral thrush. It’s crucial to use this specific code when documenting and billing for cases of oral thrush to ensure accurate record-keeping and reimbursement.
Oral thrush, or candidiasis of the mouth, is a common fungal infection that affects the mucous membranes of the mouth and throat. It is characterized by creamy white lesions, usually on the tongue or inner cheeks. While it can affect anyone, it is most common in infants, older adults, and people with weakened immune systems.
Deep Dive: Candidiasis and the B37 Category
The B37 category in ICD-10 encompasses a range of infections caused by Candida species. Understanding the different codes within this category can help differentiate between various types of candidiasis and ensure accurate coding. For example:
- B37.1: Candidiasis of lung
- B37.2: Candidiasis of skin and nails
- B37.3: Candidiasis of vulva and vagina
- B37.4: Candidiasis of other urogenital sites
- B37.5: Candidiasis of meninges
- B37.8: Candidiasis of other sites
- B37.9: Candidiasis, unspecified
Each of these codes represents a specific manifestation of Candida infection in different parts of the body. When coding for oral thrush, it is imperative to use B37.0 to accurately reflect the location of the infection.
Factors Influencing the Use of B37.0
Several factors can influence the appropriate use of the B37.0 code. These include:
- Patient Age: Oral thrush is more common in infants and older adults.
- Immune Status: Individuals with weakened immune systems, such as those with HIV/AIDS or undergoing chemotherapy, are at higher risk.
- Medication Use: Certain medications, like corticosteroids and antibiotics, can increase the risk of oral thrush.
- Underlying Conditions: Conditions like diabetes can predispose individuals to fungal infections, including oral thrush.
When documenting a case of oral thrush, it is important to consider these factors and include them in the patient’s medical record. This information can help provide a comprehensive picture of the patient’s condition and support the use of the B37.0 code.
The Role of Antifungal Medications in Treating Oral Thrush
Antifungal medications are the primary treatment for oral thrush. These medications work by inhibiting the growth of Candida fungus and reducing the severity of the infection. One commonly prescribed antifungal medication is Nystatin, available as an oral suspension. It is swished in the mouth and then swallowed, coating the affected areas and killing the fungus. Another option is Clotrimazole, available as a lozenge that dissolves slowly in the mouth, delivering the medication directly to the site of infection. For more severe cases, oral medications like Fluconazole may be prescribed.
When documenting the treatment plan, it is important to include the specific antifungal medication prescribed, the dosage, and the duration of treatment. This information is essential for tracking the patient’s progress and ensuring that the treatment is effective. In our experience, patient compliance with the prescribed medication regimen is crucial for successful treatment outcomes.
Detailed Features Analysis of Nystatin Oral Suspension
Nystatin oral suspension is a commonly prescribed antifungal medication for treating oral thrush. It works by binding to sterols in the cell membrane of the Candida fungus, causing the cell contents to leak out and leading to cell death. Here’s a detailed breakdown of its key features:
- Broad-Spectrum Antifungal Activity: Nystatin is effective against a wide range of Candida species, making it a versatile treatment option for oral thrush.
- Topical Application: As an oral suspension, Nystatin is applied directly to the affected areas in the mouth, maximizing its effectiveness and minimizing systemic side effects.
- Minimal Absorption: Nystatin is poorly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract, which means that it primarily acts locally in the mouth and has limited effects on other parts of the body.
- Well-Tolerated: Nystatin is generally well-tolerated, with few reported side effects. Common side effects may include mild nausea or diarrhea.
- Easy to Administer: The oral suspension is easy to administer, especially for infants and young children. It can be applied with a dropper or swab to the affected areas.
- Available in Various Concentrations: Nystatin oral suspension is available in various concentrations, allowing healthcare providers to tailor the dosage to the individual patient’s needs.
- Cost-Effective: Nystatin is a relatively inexpensive medication, making it an accessible treatment option for many patients.
The design and function of Nystatin oral suspension are specifically tailored to treat oral thrush effectively and safely. Its topical application, minimal absorption, and broad-spectrum antifungal activity make it a valuable tool in the fight against Candida infections in the mouth. Based on expert consensus, Nystatin remains a first-line treatment option for oral thrush.
Significant Advantages, Benefits, & Real-World Value of Accurate ICD-10 Coding
Accurate ICD-10 coding, particularly the correct application of B37.0 for oral thrush, offers numerous advantages and benefits in the healthcare ecosystem. These extend beyond mere billing and encompass patient care, research, and public health initiatives.
- Precise Billing and Reimbursement: Accurate coding ensures that healthcare providers receive appropriate reimbursement for the services they provide. Incorrect coding can lead to claim denials or underpayment, impacting the financial stability of healthcare organizations.
- Improved Patient Care: Accurate coding provides a clear and concise record of a patient’s diagnosis, treatment, and outcomes. This information is essential for coordinating care and ensuring that patients receive the appropriate treatment.
- Enhanced Data Analysis and Research: ICD-10 data is used to track health trends, identify risk factors, and evaluate the effectiveness of different treatments. Accurate coding is crucial for generating reliable data that can inform public health policies and improve healthcare outcomes.
- Effective Resource Allocation: By accurately tracking the prevalence of conditions like oral thrush, healthcare organizations can allocate resources more effectively. This includes staffing, equipment, and medications.
- Compliance with Regulations: Accurate coding is essential for complying with healthcare regulations and avoiding penalties. Government agencies and insurance companies closely monitor coding practices to ensure that they are accurate and consistent.
Users consistently report that accurate ICD-10 coding streamlines the billing process, reduces claim denials, and improves the overall efficiency of healthcare operations. Our analysis reveals that healthcare organizations that prioritize accurate coding are better positioned to provide high-quality patient care and maintain financial stability.
Comprehensive Review of ICD-10 Coding Software
Several ICD-10 coding software solutions are available to assist healthcare professionals in accurately assigning codes. One popular option is 3M’s Coding and Reimbursement System. This software offers a comprehensive database of ICD-10 codes, as well as tools for code searching, validation, and documentation. It integrates seamlessly with electronic health records (EHRs) and practice management systems, streamlining the coding process.
User Experience & Usability: 3M’s Coding and Reimbursement System is designed with user-friendliness in mind. The interface is intuitive and easy to navigate, even for users with limited coding experience. The software provides helpful prompts and guidance, ensuring that codes are assigned accurately and efficiently.
Performance & Effectiveness: This software consistently delivers accurate coding results, reducing the risk of claim denials and ensuring appropriate reimbursement. It also helps healthcare organizations stay up-to-date with the latest coding guidelines and regulations.
Pros:
- Comprehensive database of ICD-10 codes
- User-friendly interface
- Seamless integration with EHRs and practice management systems
- Accurate coding results
- Up-to-date with the latest coding guidelines
Cons/Limitations:
- Can be expensive for small practices
- Requires ongoing training and updates
- May not be suitable for all specialties
Ideal User Profile: This software is best suited for large hospitals, healthcare systems, and coding companies that require a robust and comprehensive coding solution.
Key Alternatives: Other popular ICD-10 coding software solutions include Optum EncoderPro and Find-A-Code.
Expert Overall Verdict & Recommendation: 3M’s Coding and Reimbursement System is a reliable and effective solution for ICD-10 coding. While it may be expensive for some practices, its comprehensive features and accurate coding results make it a worthwhile investment for organizations that prioritize coding accuracy and efficiency.
Navigating the Complexities: Mastering ICD-10 for Oral Thrush
In conclusion, understanding and correctly applying the ICD-10 code for oral thrush (B37.0) is paramount for accurate medical billing, effective patient care, and comprehensive data analysis. This guide has provided a detailed overview of the code, its context within the ICD-10 system, and its practical applications in healthcare settings. We hope this has clarified any confusion and empowered you with the knowledge to confidently navigate this aspect of medical coding.
As healthcare continues to evolve, staying informed about coding updates and best practices is essential. We encourage you to share your experiences with ICD-10 coding and oral thrush in the comments below, fostering a collaborative learning environment. Explore our advanced guide to medical billing for more information.