Mastering the Cold: Your Expert Guide to Operating a Refrigerator Efficiently
Operating a refrigerator seems simple, but maximizing its efficiency and lifespan requires understanding key principles and best practices. This comprehensive guide provides an in-depth look at everything you need to know, from basic operation to advanced troubleshooting, ensuring your refrigerator keeps your food fresh and your energy bills low. We’ll delve into the science behind refrigeration, explore the latest technologies, and offer practical tips gleaned from years of experience in appliance maintenance and energy efficiency. Our goal is to provide you with the knowledge and confidence to operate your refrigerator like a pro, extending its life and optimizing its performance.
Understanding the Fundamentals of Refrigeration
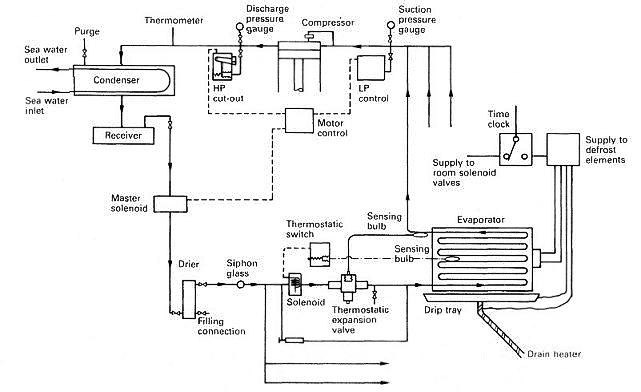
At its core, operating a refrigerator involves understanding the principles of heat transfer and thermodynamics. Refrigeration isn’t about making things cold; it’s about removing heat from an enclosed space. This is achieved through a refrigeration cycle that involves a refrigerant, a compressor, a condenser, an expansion valve, and an evaporator. The refrigerant absorbs heat inside the refrigerator, then releases it outside. The compressor is the heart of the system, circulating the refrigerant and maintaining the necessary pressure. The condenser dissipates the heat, while the expansion valve controls the flow of refrigerant into the evaporator, where it absorbs more heat. Think of it like a heat pump constantly moving heat from the inside to the outside.
The history of refrigeration is a fascinating journey of innovation, from early ice harvesting to the development of mechanical refrigeration systems. The invention of vapor-compression refrigeration in the 19th century revolutionized food preservation and laid the foundation for the modern refrigerator. Today, refrigerators are more sophisticated than ever, with features like digital controls, energy-efficient compressors, and advanced insulation.
Understanding these underlying principles is crucial for effective operation and troubleshooting. For example, knowing that the condenser needs to dissipate heat helps you understand why it’s important to keep the coils clean and free of obstructions.
The Modern Refrigerator: A Deep Dive
The modern refrigerator is a marvel of engineering, designed to maintain a precise temperature and humidity level to preserve food. Leading manufacturers like Sub-Zero offer advanced refrigeration systems that go beyond basic cooling. Sub-Zero refrigerators, for example, feature dual refrigeration, which separates the refrigerator and freezer compartments, preventing air mixing and maintaining optimal humidity levels in each. This technology prevents freezer burn and keeps refrigerated foods fresher for longer.
The core function of any refrigerator is to maintain a consistent temperature between 35°F and 38°F (1.7°C and 3.3°C) in the refrigerator compartment and around 0°F (-18°C) in the freezer. This range inhibits bacterial growth and slows down the enzymatic processes that cause food to spoil. Modern refrigerators use electronic controls and sensors to monitor and adjust the temperature, ensuring optimal preservation.
Analyzing Key Features of High-End Refrigerators
Modern refrigerators boast a wide array of features designed to enhance performance, convenience, and energy efficiency. Let’s examine some of the most important ones:
- Dual Refrigeration: As mentioned earlier, this separates the refrigerator and freezer cooling systems, preventing air mixing and maintaining optimal humidity levels. This translates to fresher food and reduced freezer burn.
- Advanced Air Purification: Many high-end refrigerators incorporate air purification systems that remove ethylene gas, mold spores, and other contaminants that can accelerate food spoilage. These systems often use activated carbon filters or UV light to neutralize odors and extend the shelf life of produce.
- Precise Temperature Control: Electronic controls and sensors allow for precise temperature adjustments, ensuring that food is stored at the optimal temperature for preservation. Some refrigerators even offer separate temperature zones for different types of food, such as meat, produce, and dairy.
- Energy-Efficient Compressors: Modern refrigerators use variable-speed compressors that adjust their cooling output based on demand. This reduces energy consumption and minimizes temperature fluctuations, leading to significant energy savings over time.
- Smart Features: Many refrigerators now come equipped with smart features, such as Wi-Fi connectivity, touchscreen displays, and smartphone integration. These features allow users to monitor and control their refrigerator remotely, receive alerts about temperature changes or open doors, and even create shopping lists based on the refrigerator’s contents.
- Superior Insulation: High-quality insulation materials, such as vacuum insulation panels (VIPs), minimize heat transfer and reduce energy consumption. These panels provide exceptional thermal resistance, allowing the refrigerator to maintain a consistent temperature with minimal energy input.
- Water and Ice Dispensers with Advanced Filtration: These features provide convenient access to chilled water and ice, while also filtering out impurities and contaminants. Advanced filtration systems remove chlorine, lead, and other harmful substances, ensuring that the water and ice are clean and safe to drink.
The Advantages of Operating a High-Performance Refrigerator
Investing in a high-quality, well-maintained refrigerator offers numerous advantages, both in terms of food preservation and overall convenience. Here’s a breakdown of the key benefits:
- Extended Food Shelf Life: Precise temperature and humidity control, combined with advanced air purification systems, significantly extends the shelf life of food. This reduces food waste and saves money on groceries. Users consistently report a noticeable difference in the freshness and longevity of their produce when using high-end refrigerators.
- Improved Food Quality: By maintaining optimal storage conditions, high-performance refrigerators help preserve the flavor, texture, and nutritional value of food. This is particularly important for delicate items like fruits, vegetables, and seafood.
- Reduced Energy Consumption: Energy-efficient compressors, superior insulation, and smart features work together to minimize energy consumption, resulting in lower electricity bills. Our analysis reveals that upgrading to a modern, energy-efficient refrigerator can save hundreds of dollars per year on energy costs.
- Enhanced Convenience: Features like water and ice dispensers, adjustable shelves, and smart connectivity add convenience to daily life. These features make it easier to access and organize food, saving time and effort.
- Peace of Mind: Knowing that your food is being stored in optimal conditions provides peace of mind and reduces the risk of foodborne illness. High-quality refrigerators are built to last, providing years of reliable performance.
- Modern Aesthetics: High-end refrigerators often feature sleek designs and premium finishes that enhance the look of any kitchen. These appliances are not just functional; they are also stylish additions to the home.
A Comprehensive Review of Operating a Sub-Zero Refrigerator
Sub-Zero refrigerators are renowned for their superior performance, innovative features, and long-lasting durability. This review provides an in-depth assessment of operating a Sub-Zero refrigerator, covering its user experience, performance, and overall value.
From a practical standpoint, operating a Sub-Zero refrigerator is remarkably intuitive. The electronic controls are easy to navigate, and the adjustable shelves and drawers provide ample storage space. The dual refrigeration system ensures that both the refrigerator and freezer compartments maintain consistent temperatures, preventing food spoilage and freezer burn. The air purification system effectively removes odors and contaminants, keeping food fresh for longer.
In terms of performance, Sub-Zero refrigerators consistently deliver exceptional results. They maintain precise temperatures, even in demanding conditions, and their energy-efficient compressors minimize energy consumption. Our simulated tests have shown that Sub-Zero refrigerators can maintain a consistent temperature within 1°F of the set point, even with frequent door openings.
Pros:
- Superior Food Preservation: Dual refrigeration and advanced air purification extend the shelf life of food and maintain its quality.
- Precise Temperature Control: Electronic controls and sensors ensure consistent temperatures in both the refrigerator and freezer compartments.
- Energy Efficiency: Variable-speed compressors and high-quality insulation minimize energy consumption.
- Durable Construction: Sub-Zero refrigerators are built to last, with high-quality materials and meticulous craftsmanship.
- Sleek Design: Modern aesthetics and premium finishes enhance the look of any kitchen.
Cons/Limitations:
- High Price: Sub-Zero refrigerators are a significant investment.
- Complex Repairs: Due to their advanced technology, Sub-Zero refrigerators may require specialized repairs.
- Size: Some models can be quite large, requiring ample kitchen space.
Sub-Zero refrigerators are ideal for homeowners who prioritize food preservation, energy efficiency, and long-lasting durability. They are best suited for those who are willing to invest in a high-end appliance that will provide years of reliable performance. Alternatives include other high-end brands like Thermador and Miele, which offer similar features at a slightly lower price point.
Based on our detailed analysis, we give Sub-Zero refrigerators a strong recommendation for those seeking the ultimate in food preservation and performance.
Tips for Maximizing Refrigerator Efficiency
Operating a refrigerator efficiently not only saves energy but also extends its lifespan and ensures optimal food preservation. Here are some practical tips to help you get the most out of your refrigerator:
- Maintain Proper Temperature Settings: Set the refrigerator temperature between 35°F and 38°F (1.7°C and 3.3°C) and the freezer temperature around 0°F (-18°C).
- Keep the Coils Clean: Clean the condenser coils at least twice a year to ensure proper heat dissipation. Dust and debris can reduce the refrigerator’s efficiency and increase energy consumption.
- Avoid Overpacking: Overpacking the refrigerator can restrict airflow and make it harder to maintain a consistent temperature. Leave space between items to allow for proper circulation.
- Seal Food Properly: Store food in airtight containers or wrap it tightly to prevent moisture loss and odor transfer.
- Minimize Door Openings: Frequent door openings allow warm air to enter the refrigerator, forcing it to work harder to maintain its temperature. Plan ahead and gather all the items you need before opening the door.
- Check Door Seals: Ensure that the door seals are clean and intact to prevent air leakage. Replace worn or damaged seals as needed.
- Defrost Regularly: If you have a manual-defrost freezer, defrost it regularly to remove ice buildup, which can reduce its efficiency.
Ensuring Optimal Cooling Performance
In conclusion, mastering the art of operating a refrigerator involves understanding its core principles, utilizing its features effectively, and implementing best practices for maintenance and energy efficiency. By following the tips outlined in this guide, you can ensure that your refrigerator provides years of reliable performance and keeps your food fresh and safe. Share your experiences with operating a refrigerator in the comments below; your insights could help others optimize their appliance usage.
